xlua框架导入和AB包相关准备 Unity-Technologies/AssetBundles-Browser: Editor tool for viewing and debugging asset bundle contents before and after builds (github.com)
Tencent/xLua: xLua is a lua programming solution for C# ( Unity, .Net, Mono) , it supports android, ios, windows, linux, osx, etc. (github.com)
[AB包管理器](AB包学习笔记 | 紫地丁的个人博客 (purpleditine.top) )
Lua解析器 为了实现热更新,我们需要使用Lua和C#的相互调用
我们可以使用xlua的lua解析器直接调用Lua代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 using UnityEngine;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson1LuaEnv : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaEnv env = new (); env.DoString("print('Hello World!')" ); } } }
其他lua解析器常用方法
1 2 env.Tick(); env.Dispose();
也可以执行lua脚本
我们可以在Resources文件夹下创建一个名为Main.lua.txt的文件
1 2 3 print ('这是一个lua脚本' )a = 1 ; print (a)
然后调用env.DoString("require('Main')")
猜测该程序内部用Resources.Load查找文件
Lua文件加载重定向 在实际开发中我们明显不能用刚才的方法,或者说我们需要自定义lua文件的路径并且文件后缀应该是.lua
我们可以使用AddLoader方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 using UnityEngine;using UnityEngine.Windows;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson2Loader : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaEnv env = new (); env.AddLoader(MyCustomLoader); env.DoString("require('Main')" ); } private byte [] MyCustomLoader (ref string fileName { string path = Application.dataPath + "/Scripts/Lua/" + fileName + ".lua" ; Debug.Log(path); if (File.Exists(path)) { return File.ReadAllBytes(path); } Debug.LogWarning("重定向失败" +path); return null ; } } }
AddLoader会添加一个委托算法,用于查找lua文件,可以添加多个。当我们调用env.DoString(“require(‘Main’)”),程序会首先执行一遍所有的我们添加过的委托,如果找不到文件,再查找默认的Resources文件夹
Lua解析器管理器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 using UnityEngine;using System.IO;using XLua;namespace Tool { public class LuaManager : Singleton <LuaManager > { private LuaEnv _luaEnv; private LuaEnv LuaEnv { get { if (_luaEnv is not null ) return _luaEnv; _luaEnv = new LuaEnv(); _luaEnv.AddLoader(MyCustomLoader); _luaEnv.AddLoader(MyCustomABLoader); return _luaEnv; } } public LuaTable Global => LuaEnv.Global; public void DoScript (string fileName { LuaEnv.DoString($"require('{fileName} ')" ); } public void DoString (string str { LuaEnv.DoString(str); } public void Tick () { LuaEnv.Tick(); } public void Dispose () { if (_luaEnv is null ) return ; _luaEnv.Dispose(); _luaEnv = null ; } private byte [] MyCustomLoader (ref string fileName { var path = Application.dataPath + "/Scripts/Lua/" + fileName + ".lua" ; Debug.Log(path); if (File.Exists(path)) { return File.ReadAllBytes(path); } Debug.LogWarning("重定向失败" +path); return null ; } private byte [] MyCustomABLoader (ref string fileName { var lua = ABManager.Instance.LoadResource<TextAsset>("lua" , fileName + ".lua" ); if (lua is not null ) return lua.bytes; Debug.LogWarning("重定向失败,文件名:" +fileName); return null ; } } }
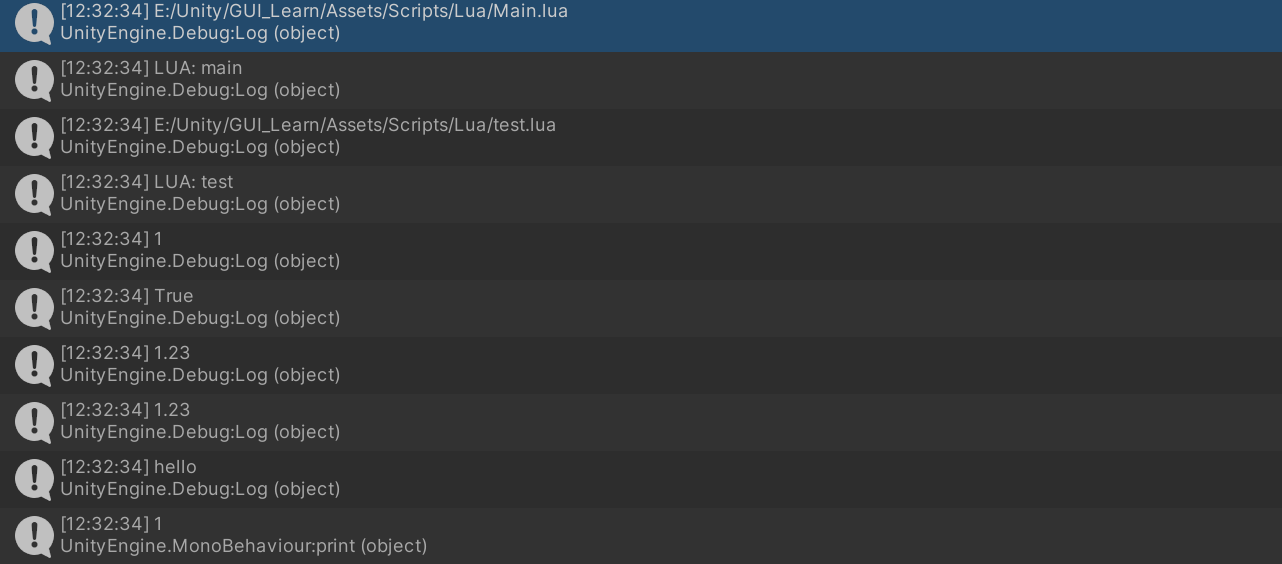
全局变量的获取 1 2 3 print ("main" )require ("test" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 print ("test" )testNumber = 1 testBool = true testFloat = 1.23 testString = "hello"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 using Tool;using UnityEngine;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson4CallLua : MonoBehaviour { private string a; private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); var i = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<int >("testNumber" ); var b = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<bool >("testBool" ); var f = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<float >("testFloat" ); var d = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<double >("testFloat" ); var s = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<string >("testString" ); Debug.Log(i); Debug.Log(b); Debug.Log(f); Debug.Log(d); Debug.Log(s); LuaManager.Instance.Global.Set("testNumber" ,33 ); print(i); } } }
全局函数的获取 1 2 3 print ("main" )require ("test" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 print ("test" )testFun1 = function () print ("无参无返回" ) end testFun2 = function (a) print ("有参有返回" ) return a +1 end testFun3 = function (a) print ("多返回" ) return 1 ,2 ,false ,"hello" ,a end testFun4 = function (a,...) print ("变长参数" ) print (a) arg = {...} for k,v in pairs (arg )do print (k,v) end end
C#调用无参无返回lua函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 using System;using Tool;using UnityEngine;using UnityEngine.Events;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson5CallFunction : MonoBehaviour { public delegate void CustomCall () private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); UnityAction ua = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<UnityAction>("testFun1" ); CustomCall call = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CustomCall>("testFun1" ); Action ac = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<Action>("testFun1" ); LuaFunction lf = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<LuaFunction>("testFun1" ); ua(); call(); ac(); lf.Call(); } } }
C#调用有参有返回lua函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 using Tool;using UnityEngine;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson5CallFunction : MonoBehaviour { [CSharpCallLua ] public delegate int CustomCall (int a private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); CustomCall call = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CustomCall>("testFun2" ); Func<int ,int > func = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<Func<int ,int >>("testFun2" ); LuaFunction lf2 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<LuaFunction>("testFun2" ); Debug.Log(lf2.Call(3 )[0 ]); func(3 ); call(3 ); } } }
如果出现以下报错,需要点击Xlua/Generate Code
C#调用多返回值lua函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 using Tool;using UnityEngine;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson5CallFunction : MonoBehaviour { [CSharpCallLua ] public delegate int CustomCall (int a, out int b, out bool c, out string d,out int e [CSharpCallLua ] public delegate int CustomCall2 (int a, ref int b, ref bool c, ref string d,ref int e private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); CustomCall call = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CustomCall>("testFun3" ); CustomCall2 call2 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CustomCall2>("testFun3" ); LuaFunction lf3 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<LuaFunction>("testFun3" ); int b=0 ; bool c=false ; string d="" ; int e=0 ; Debug.Log(call(1 , out b, out c, out d, out e)); Debug.Log(call2(100 ,ref b,ref c,ref d,ref e)); var objs = lf3.Call(100 ); foreach (var obj in objs) { Debug.Log(obj); } } } }
C#调用变长参数lua函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 using Tool;using UnityEngine;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { [CSharpCallLua ] public delegate void CustomCall (string a, params object [] args public class Lesson5CallFunction : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); LuaFunction lf4 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<LuaFunction>("testFun4" ); lf4.Call(1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 54 , 5 , 6 ); } } }
List和Dictionary映射table 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 print ("test" )testList = {1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 } testList2 = {"hello" ,true ,1 ,1.2 } testDic = { ["1" ] = 1 , ["2" ] = 2 , ["3" ] = 3 , ["4" ] = 4 } testDic2 = { ["1" ] = 1 , [true ] = 1 , [false ] = true , ["123" ] = false , }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 using System.Collections.Generic;using Tool;using UnityEngine;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson6CallListDic : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); List<int > list = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<List<int >>("testList" ); foreach (var item in list) { Debug.Log(item); } List<object > list2 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<List<object >>("testList2" ); foreach (var item in list2) { Debug.Log(item); } Dictionary<string , int > dic = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<Dictionary<string , int >>("testDic" ); foreach (var item in dic) { Debug.Log(item); } Dictionary<object ,object > dic2 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<Dictionary<object , object >>("testDic2" ); foreach (var item in dic2) { Debug.Log(item); } } } }
类映射table 类中的成员名和table中的成员名要一致,总数可以多也可以少
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 print ("test" )testClass = { testInt = 2 , testBool = true , testFloat = 1.2 , testString = "hello" , testFun = function () print ("Hello World" ) end , testInClass = { testInInt = 1 ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 using Tool;using UnityEngine;using UnityEngine.Events;namespace xLua_Learn { public class InClass { public int testInInt; } public class CallLUaClass { public int testInt; public bool testBool; public float testFloat; public string testString; public UnityAction testFun; public InClass testInClass; } public class Lesson7CallClass : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); CallLUaClass obj = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CallLUaClass>("testClass" ); Debug.Log(obj.testString); obj.testFun(); Debug.Log(obj.testInClass.testInInt); } } }
接口映射table 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 using Tool;using UnityEngine;using UnityEngine.Events;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { [CSharpCallLua ] public interface ICSharpCallInterface { int testInt { get ; set ; } bool testBool { get ; set ; } float testFloat { get ; set ; } string testString { get ; set ; } UnityAction testFun { get ; set ; } } public class Lesson8CallInterface : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); ICSharpCallInterface obj = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<ICSharpCallInterface>("testClass" ); Debug.Log(obj.testInt); obj.testFun(); Debug.Log(obj.GetType()); } } }
首先我们一定不能认为我们用接口实例化了一个对象,似乎是xlua自己在生成的代码中定义了一个类,使这个类继承我们的接口,返回了这个类的对象
用接口映射table和类有个明显的不同
用类映射table,两次用不同的对象映射,类似”值传递”,其中一个对象的改变不会影响另一个对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private void Start (){ LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); CallLUaClass obj = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CallLUaClass>("testClass" ); CallLUaClass obj2 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<CallLUaClass>("testClass" ); Debug.Log(obj.testString); Debug.Log(obj2.testString); obj.testString = "123" ; Debug.Log(obj2.testString); }
而用接口映射table,类似”引用传递”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); ICSharpCallInterface obj = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<ICSharpCallInterface>("testClass" ); ICSharpCallInterface obj2 = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<ICSharpCallInterface>("testClass" ); Debug.Log(obj.testString); Debug.Log(obj2.testString); obj.testString = "123" ; Debug.Log(obj2.testString);
推测每次使用类映射table时,xlua都返回一个新的类对象,当使用接口映射table时,第一次一个返回xlua生成的类的对象,以后的每次映射都使用这个对象
LuaTable映射table 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 using Tool;using UnityEngine;using UnityEngine.Events;using XLua;namespace xLua_Learn { public class Lesson9CallLuaTable : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { LuaManager.Instance.DoScript("Main" ); LuaTable table = LuaManager.Instance.Global.Get<LuaTable>("testClass" ); Debug.Log(table.Get<int >("testInt" )); table.Get<UnityAction>("testFun" )(); table.Dispose(); } } }
用LuaTable映射table也类似”引用传递”
记得用完要Dispose
Lua调用C#类 lua调用C#类固定套路:CS.命名空间.类名
直接在类名后加”()”,即调用构造
1 2 3 local obj1 = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject()
调用该脚本,场景上即生成空物体
如有参数,同理
1 local obj2 = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject("hello" )
可以用类似宏的方式简写对类的引用,猜测本质就是简单的存储变量
这也是一种优化的办法
1 2 3 GameObject = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject local obj3 = GameObject("world" )
类中的静态成员和对象的成员变量可以直接使用.来调用
1 2 3 local obj4 = GameObject.Find("hello" )Debug = CS.UnityEngine.Debug Debug.Log(obj4.transform.position)
如果使用对象的成员方法,要加”:”
1 2 Vector3 = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3 obj4.transform:Translate(Vector3.right)
使用lua调用C#自定义类,即固定套路:CS.命名空间.类名
如果没有命名空间,不加即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class Test { public void Speak (string str { Debug.Log("Test1" +str); } }
1 2 local t = CS.Test()t:Speak("test Speak" )
如果是继承MonoBehaviour的类,如下
1 obj4:AddComponent(typeof(CS.UnityEngine.UI.Image))
lua不支持无参泛型函数
Lua调用C#枚举 枚举的调用规则同类的调用规则:CS.命名空间.枚举名
1 2 3 4 PrimitiveType = CS.UnityEngine.PrimitiveType GameObject = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject local obj = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube)
也可以将其他的值转换为枚举值
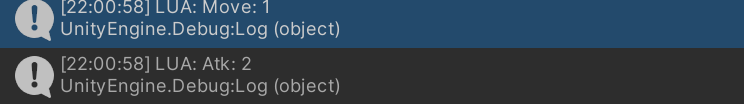
1 2 3 4 public enum MyEnum{ Idle,Move,Atk }
1 2 3 4 5 6 MyEnum = CS.MyEnum local a = MyEnum.__CastFrom(1 )print (a)local b = MyEnum.__CastFrom("Atk" )print (b)
Lua调用C#数组,List和Dictionary 1 2 3 4 5 6 public class Lesson3 { public int [] array = new [] { 1 , 2 , 3 }; public List<int > list = new (); public Dictionary<string ,int > dic = new (); }
调用数组 以下lua代码中obj是一个userdata类型的变量,保留了源语言的结构,C#怎么用,lua中就怎么用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 local obj = CS.Lesson3()print (obj.array[0 ])for i = 0 ,obj.array.Length-1 do print (obj.array[i]) end print (obj.array.Length)local array2 = CS.System.Array.CreateInstance(typeof(CS.System.Int32),10 )print (array2.Length)
调用List 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 local obj = CS.Lesson3()obj.list:Add(1 ) obj.list:Add(2 ) obj.list:Add(3 ) print (obj.list.Count)for i = 0 ,obj.list.Count-1 do print (obj.list[i]) end local list2 = CS.System.Collections.Generic["List`1[System.String]" ]()local List_String = CS.System.Collections.Generic.List(CS.System.String)local list3 = List_String()
调用Dictionary 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 local obj = CS.Lesson3()obj.dic:Add("hello" ,1 ) obj.dic:Add("world" ,2 ) for k,v in pairs (obj.dic) do print (k,v) end local Dic_String_Vector3 = CS.System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary(CS.System.String,CS.UnityEngine.Vector3)local dic = Dic_String_Vector3()
Lua调用C#拓展方法 如果想要在Lua中使用拓展方法,一定要在工具类前面加上特性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Lesson4 { public string name = "hello" ; public void Speak (string str { Debug.Log(str); } public static void Eat () { Debug.Log("eat" ); } } [LuaCallCSharp ] public static class Tools { public static void Move (this Lesson4 obj { Debug.Log(obj.name +"移动" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lesson4 = CS.Lesson4 Lesson4.Eat() local obj = Lesson4()obj:Speak("hahaha" ) obj:Move()
建议lua中要使用的类都加特性[LuaCallCSharp],可以提升性能
Lua调用C#ref/out函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Lesson5 { public int RefFun (int a, ref int b, ref int c,int d { b = a + d; c = a - d; return b + c; } public int OutFun (int a, out int b, out int c, int d { b = a + d; c = a - d; return b - c; } public int RefOutFun (int a, ref int b, out int c, int d { b = a + d; c = a - d; return a + b + c + d; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lesson5 = CS.Lesson5 local obj = Lesson5()local a,b,c = obj:RefFun(1 ,0 ,0 ,1 )local a,b,c = obj:OutFun(1 ,2 )local a,b,c = obj:RefOutFun(2 ,0 ,2 )
lua使用C#重载函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Lesson6 { public int Calc () { return 100 ; } public int Calc (int a, int b { return a + b; } public int Calc (int a { return a; } public float Calc (float a { return a; } }
虽然Lua自己不支持重载,但支持C#的重载
以下重载直接书写即可
1 2 3 4 5 local obj = CS.Lesson6()print (obj:Calc())print (obj:Calc(15 ,1 ))
但lua对数字类型的精度不敏感,以下代码使用会出现问题
1 2 print (obj:Calc(10 ))print (obj:Calc(10.2 ))
如果实在要实现对数字精度不同的重载函数的支持,可以用反射的原理
1 2 3 4 5 6 local m1 = typeof(CS.Lesson6):GetMethod("Calc" ,{typeof(CS.System.Int32)})local m2 = typeof(CS.Lesson6):GetMethod("Calc" ,{typeof(CS.System.Single)})local f1 = xlua.tofunction(m1)local f2 = xlua.tofunction(m2)print (f1(obj,10 )) print (f2(obj,10.2 ))
以上方法能不用就不用
Lua调用C#委托和事件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Lesson7 { public UnityAction del; public event UnityAction eventAction; public void DoEvent () { eventAction?.Invoke(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 local obj = CS.Lesson7()local fun = function () print ("lua function" ) end obj.del = fun obj.del = obj.del + fun obj.del(); obj.del = obj.del - fun obj.del() obj.del = nil local fun2 = function () print ("lua event function" ) end obj:eventAction("+" ,fun2) obj:eventAction("+" ,fun2) obj:DoEvent() obj:eventAction("-" ,fun2) obj:DoEvent()
Lua调用C#二维数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class Lesson8 { public int [,] array = new int [2 , 3 ] { { 1 , 2 , 3 }, { 4 , 5 , 6 } }; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 local obj = CS.Lesson8()print ("行:" ..obj.array:GetLength(0 ))print ("列:" ..obj.array:GetLength(1 ))print (obj.array:GetValue(0 ,0 ))print (obj.array:GetValue(1 ,0 ))for i =0 ,obj.array:GetLength(0 )-1 do for j =0 ,obj.array:GetLength(1 )-1 do print (obj.array:GetValue(i,j)) end end
Lua的nil和C#的null的比较 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 GameObject = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject Rigidbody = CS.UnityEngine.Rigidbody local obj = GameObject("test add sprict" )local rig = obj:GetComponent(typeof(Rigidbody))print (rig)if rig == nil then print ("null == nil" ) rig = obj:AddComponent(typeof(Rigidbody)) end print (rig)
在这个测试中我们发现,null和nil是不能进行==比较的
但如果我们这样写代码,就可以成功判空
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 GameObject = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject Rigidbody = CS.UnityEngine.Rigidbody local obj = GameObject("test add sprict" )local rig = obj:GetComponent(typeof(Rigidbody))print (rig)if rig:Equals(nil ) then rig = obj:AddComponent(typeof(Rigidbody)) end print (rig)
由此,写一个全局函数,以方便判空
1 2 3 function IsNull (obj) return obj == nil or obj:Equals(nil ) end
1 2 3 if IsNull(rig) then rig = obj:AddComponent(typeof(Rigidbody)) end
或者,我们可以在C#方面判空,使用拓展方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [LuaCallCSharp ] public static class Lesson9 { public static bool IsNull (this Object obj { return obj == null ; } }
1 2 3 if rig:IsNull() then rig = obj:AddComponent(typeof(Rigidbody)) end
在我的测试中,如果拓展方法的this后写的是object,那么这个函数会不起作用,如果是Object就可以,原因未知,目前只能断定与Object的命名空间无关
Lua和系统类或委托相互使用 此前,我们在使用lua调用C#时,经常需要用到[LuaCallCSharp]特性,但当我们需要系统类或第三方代码时,更改源代码困难
比如,如果我们希望在一个脚本的事件中加一个委托,如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 GameObject = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject UI=CS.UnityEngine.UI local slider = GameObject.Find("Slider" )local sliderScript = slider:GetComponent(typeof(UI.Slider))sliderScript.onValueChanged:AddListener(function (f) print (f) end )
Unity报错,希望我们在UnityEngine.Events.UnityAction类型的委托前加特性,这显然是不可能的
此时,我们用如下方法解决这个需求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public static class Lesson10 { [CSharpCallLua ] public static List<Type> CSharpCallLuaList = new () { typeof (UnityAction<float >) }; }
再次运行以上lua即可生效
[CSharpCallLua]和[LuaCallCSharp]都可使用此方法,新增的要添加特性的类型直接加入list即可
Lua调用C#协程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 util = require ("xlua.util" ) GameObject = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject WaitForSeconds = CS.UnityEngine.WaitForSeconds local obj = GameObject("Coroutine" )local mono = obj:AddComponent(typeof(CS.LuaCallCSharp.LuaCallCSharp))fun = function () local a = 1 while true do print (a) a = a + 1 coroutine .yield (WaitForSeconds(1 )) if a>10 then mono:StopCoroutine(b) end end end b = mono:StartCoroutine(util.cs_generator(fun))
Lua调用C#泛型函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Lesson12 { public interface ITest {} public class TestFather {} public class TestChild : TestFather ,ITest {} public void TestFun1 <T >(T a, T b ) where T : TestFather { Debug.Log("有参数有约束的泛型方法" ); } public void TestFun2 <T >(T a ) { Debug.Log("有参数无约束的泛型方法" ); } public void TestFun3 <T >() where T : TestFather { Debug.Log("无参数有约束的泛型方法" ); } public void TestFun4 <T >(T a, T b ) where T : ITest { Debug.Log("有参数有约束接口的泛型方法" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 local obj = CS.Lesson12()local child = CS.Lesson12.TestChild()local father = CS.Lesson12.TestFather()obj:TestFun1(child,father) obj:TestFun1(father,child)
综上,lua只支持有参数,有class约束的泛型方法
我们可以使用一个方法使不支持的泛型函数变得可以使用,其原理是用xlua提供的方法得到一个泛型函数的泛型确定后的普通函数
如果你使用的是mono打包,可以使用这个方法
如果是il2cpp,泛型参数是引用类型才可以使用,如果泛型参数是值类型,除非C#方面已经调用过同类型的反省参数,lua中才可以使用
1 2 3 4 local testFun2 = xlua.get_generic_method(CS.Lesson12,"TestFun2" )local testFun2_R = testFun2(CS.System.Int32)testFun2_R(obj,1 )