基本概念 IP地址 如果有两个处于局域网中的设备,怎么将信息准确的从一台设备传递给另一台设备?
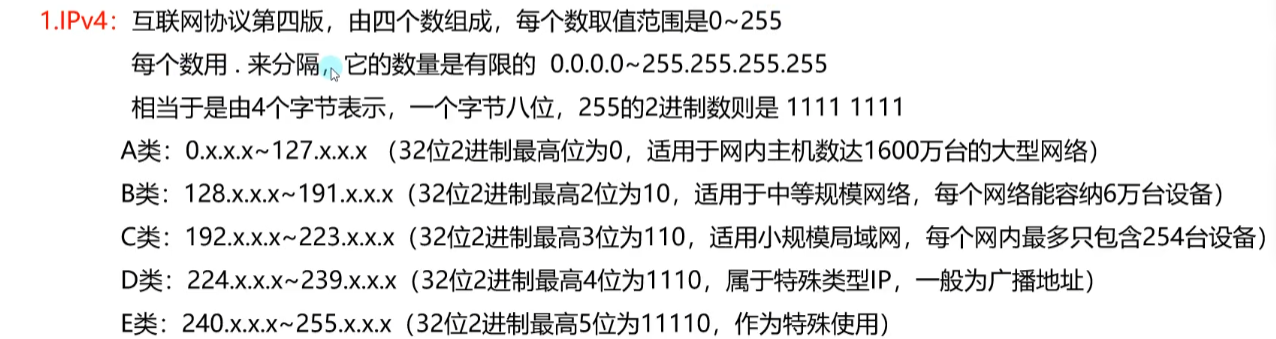
IP地址是一种统一的地址格式,是设备在网络中的具体地址
按协议分类
IPv6可以为世界上的每一粒沙子定义IP地址
按使用范围分类
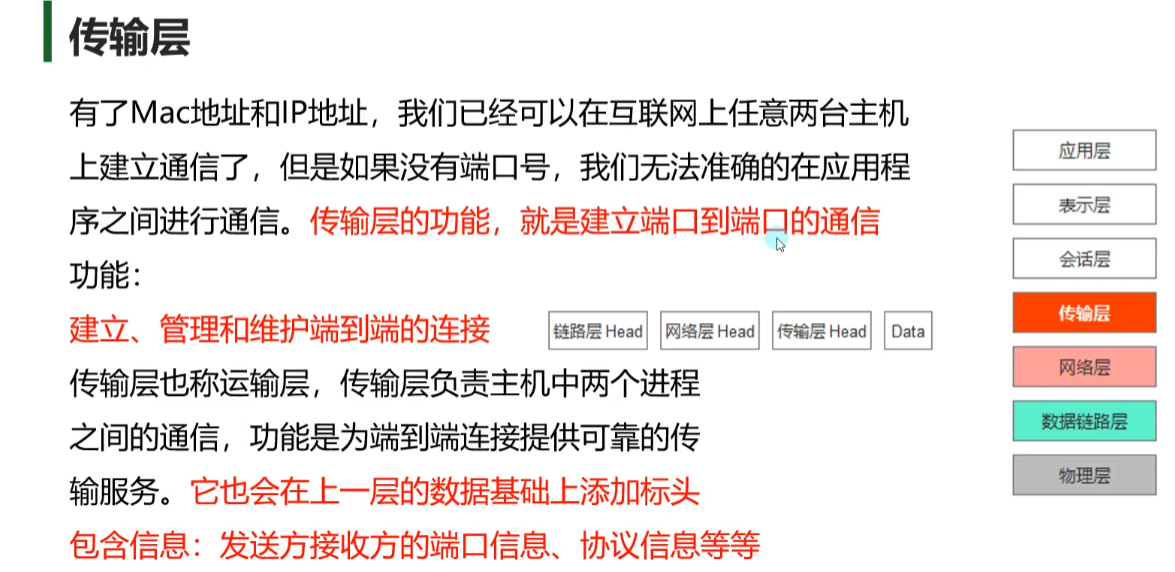
端口号 端口号用来区分设备的应用程序
Mac地址
客户端和服务端 客户端 即用户使用的设备,泛指客户端应用程序
服务端
数据通信模型 数据通信模型
分散式
集中式
分布式
C/S模型 即client/server
B/S模型 即browse/server
P2P模型
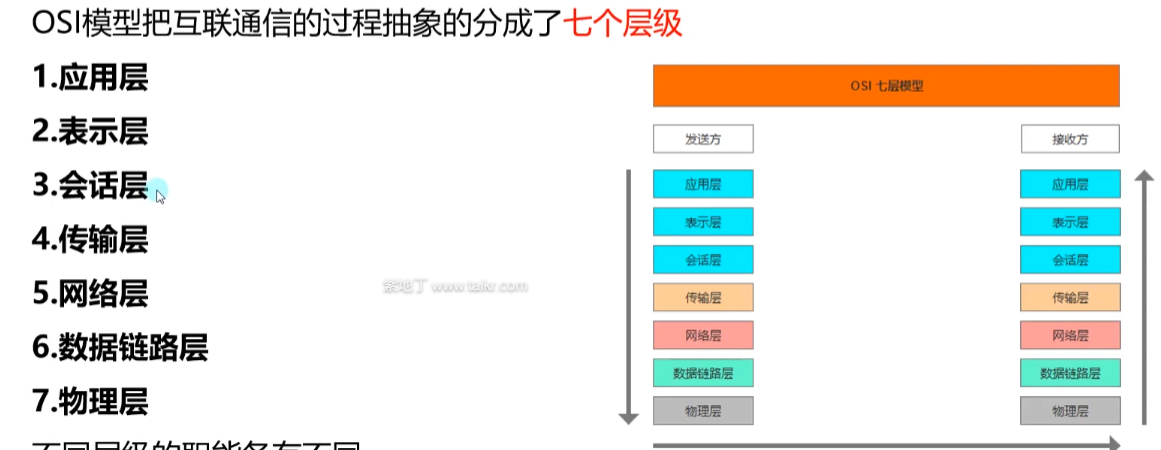
网络协议概述
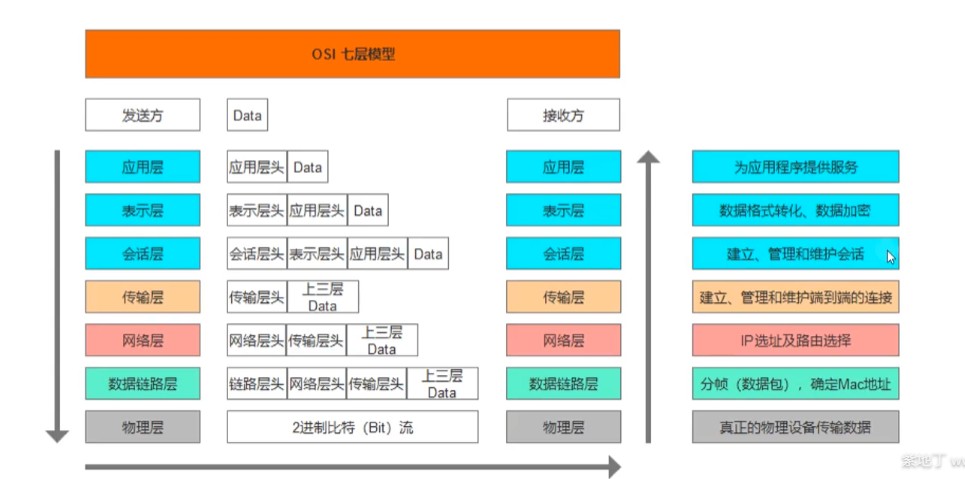
OSI模型
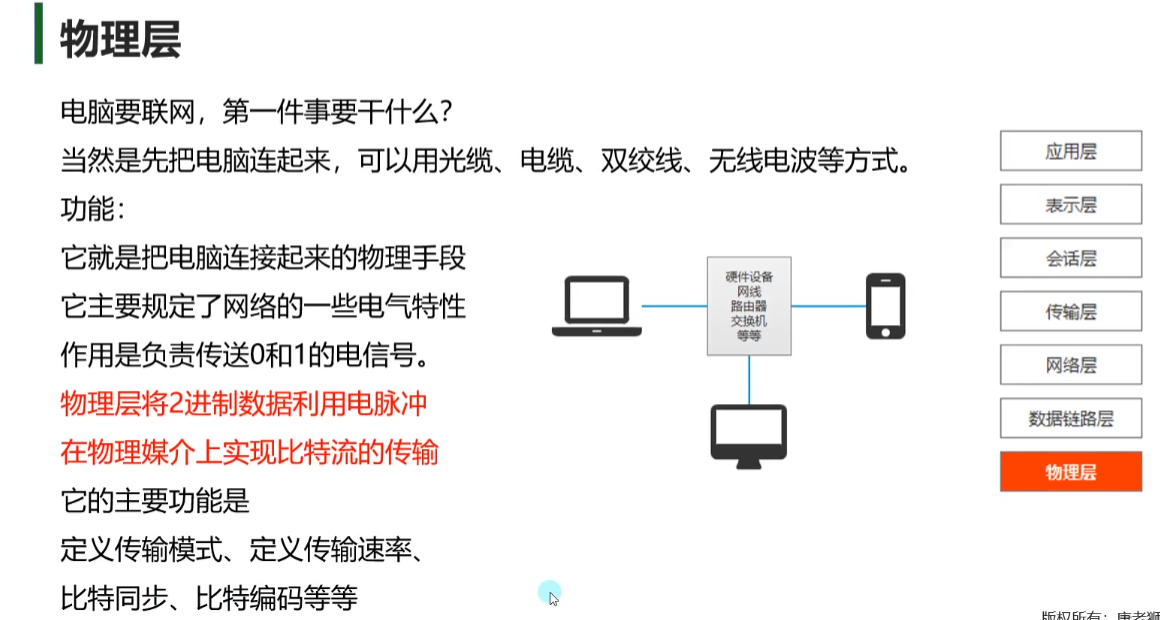
OSI各层的作用 物理层
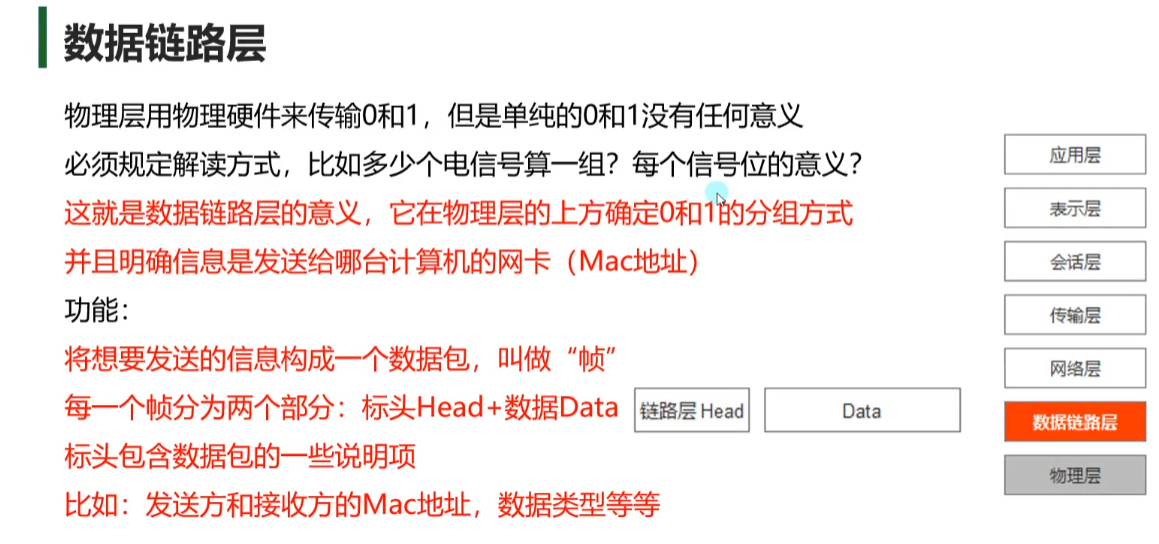
数据链路层
网络层
传输层
应用层
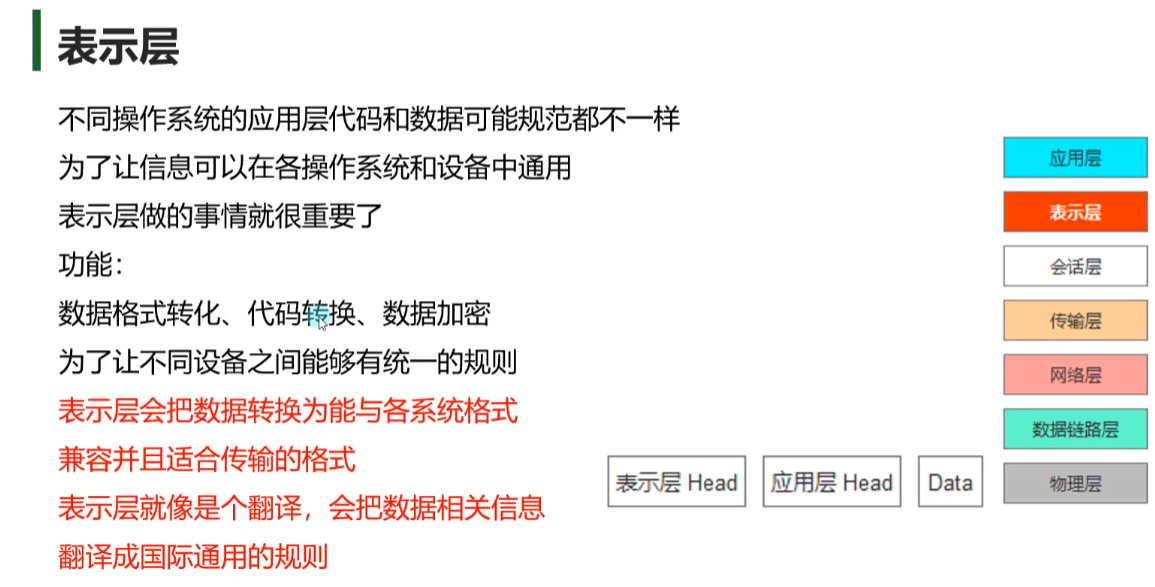
表示层
会话层
TCP/IP协议
TCP/IP协议的规则 TCP/IP基于OSI设计
TCP和UDP TCP:传输控制协议
UDP:用户数据报协议
TCP
“三次握手”建立连接,”四次挥手”断开连接
UDP
网络游戏通信方案概述 弱联网和强联网 弱联网:游戏不会频繁的进行数据通信,客户端和服务端之间每次连接只处理一次请求
强联网:游戏会频繁的和服务端进行通信,会一直和服务端保持连接状态,不停的交换数据
长连接和短连接 按照网络游戏通信特点划分
短连接
通信方式:HTTP,HTTPS(本质上是TCP)
长连接
通信方式:TCP,UDP
Socket,HTTP,FTP Socket 网络套接字,是对网络中不同主机上应用进程之间进行双向通信的端点的抽象
主要用来完成长连接
HTTP/HTTPS 超文本传输协议
主要用来完成短连接
FTP 文件传输协议
主要用来完成文件的上传和下载
IP地址和端口类 IPAddress类 使用byte数组进行初始化
1 2 byte [] ipAddress = new byte [] { 118 , 102 , 111 , 11 };IPAddress ip1 = new IPAddress(ipAddress);
使用long初始化
1 IPAddress ip2 = new IPAddress(0x79666F0B );
推荐初始化方式,字符串转换
1 IPAddress ip3 = IPAddress.Parse("118,102.111.11" );
特殊ip地址:127.0.0.1 代表本机地址
IPEndPoint类 IPEndPoint表现为ip地址和端口号的组合
1 IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(ip3,8008 );
域名解析 什么是域名解析 将域名解析成ip
为了方便记忆,采用域名标识站点地址
域名的解析工作由DNS(域名系统)服务器完成
IPHostEntry类 域名解析后的返回值,用来获取ip地址,主机名等信息
该类不会自己声明,都是作为某些方法返回值返回信息
DNS类 一个静态类,可以使用它根据域名获取ip地址
获取本机系统的主机名
1 PFCLog.Info(Dns.GetHostName());
1 [PFC_Info]:LAPTOP-EKSLMM8U
获取指定域名可的ip信息
由于获取远程主机信息需要进行网络通信,所以可能会阻塞主线程
1 2 3 4 5 6 IPHostEntry entry = Dns.GetHostEntry("www.purpleditine.top" ); foreach (var t in entry.AddressList){ PFCLog.Info(t); }
异步获取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private async void GetHostEntry (){ Task<IPHostEntry> task = Dns.GetHostEntryAsync("www.purpleditine.top" ); await task; foreach (var t in task.Result.AddressList) { PFCLog.Info(t); } }
序列化和反序列化二进制数据 网络通信中传输的数据 网络通信中传输的是二进制数据,所以我们需要将类对象信息序列化为二进制数据(一般为byte字节数组)
我们以前在C#中使用BinaryFormatter类将C#类转换为字节数组,但在此处我们不使用这种办法,因为BinaryFormatter不兼容其他语言,而客户端和服务端的语言大多数时候是不同的
序列化与反序列化 如果不使用BinaryFormatter,将类对象转换为二进制就需要我们自己处理
首先,我们需要明确字节数组的容量
对象中出现了string类型的变量,所以当我们传输数据的时候,要在string数据之前传输string的长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class PlayerInfo { public int lev; public string name; public short atk; public bool sex; }
对于以上这个类,其对象内存应占用4+4(name长度)+name长度+2+1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public byte [] Class2Byte (PlayerInfo info ){ int byteLength = sizeof (int ) + sizeof (int ) + Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(info.name).Length + sizeof (short ) + sizeof (bool ); byte [] playerBytes = new byte [byteLength]; int index = 0 ; BitConverter.GetBytes(info.lev).CopyTo(playerBytes,index); index += 4 ; byte [] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(info.name); int num = strBytes.Length; BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes,index); index += 4 ; strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes,index); index += num; BitConverter.GetBytes(info.atk).CopyTo(playerBytes,index); index += 2 ; BitConverter.GetBytes(info.sex).CopyTo(playerBytes,index); index += 1 ; return playerBytes; }
反序列化同理
我们写一个数据基类来方便数据的序列化和反序列化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 using System;using System.Text;namespace NetLearn.Data { public abstract class BaseData { #region 序列化 public abstract int GetBytesNum () public abstract byte [] Writing () protected void WriteInt (byte [] bytes,int value ,ref int index { BitConverter.GetBytes(value ).CopyTo(bytes,index); index += 4 ; } protected void WriteShort (byte [] bytes,short value ,ref int index { BitConverter.GetBytes(value ).CopyTo(bytes,index); index += 2 ; } protected void WriteLong (byte [] bytes,long value ,ref int index { BitConverter.GetBytes(value ).CopyTo(bytes,index); index += 8 ; } protected void WriteFloat (byte [] bytes,float value ,ref int index { BitConverter.GetBytes(value ).CopyTo(bytes,index); index += 4 ; } protected void WriteByte (byte [] bytes,byte value ,ref int index { bytes[index] = value ; index += 1 ; } protected void WriteBool (byte [] bytes,bool value ,ref int index { BitConverter.GetBytes(value ).CopyTo(bytes,index); index += 1 ; } protected void WriteString (byte [] bytes,string value ,ref int index { byte [] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(value ); WriteInt(bytes,strBytes.Length,ref index); strBytes.CopyTo(bytes,index); index += strBytes.Length; } protected void WriteData (byte [] bytes, BaseData value , ref int index { value .Writing().CopyTo(bytes,index); index += value .GetBytesNum(); } #endregion public abstract int Reading (byte [] bytes,int beginIndex = 0 protected int ReadInt (byte [] bytes, ref int index { int value = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, index); index += 4 ; return value ; } protected short ReadShort (byte [] bytes, ref int index { short value = BitConverter.ToInt16(bytes, index); index += 2 ; return value ; } protected long ReadLong (byte [] bytes, ref int index { long value = BitConverter.ToInt64(bytes, index); index += 8 ; return value ; } protected float ReadSingle (byte [] bytes, ref int index { float value = BitConverter.ToSingle(bytes, index); index += 4 ; return value ; } protected byte ReadByte (byte [] bytes, ref int index { byte value = bytes[index]; index += 1 ; return value ; } protected bool ReadBool (byte [] bytes, ref int index { bool value = BitConverter.ToBoolean(bytes, index); index += 1 ; return value ; } protected string ReadString (byte [] bytes, ref int index { int length = ReadInt(bytes, ref index); string value = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, index, length); index += length; return value ; } protected T ReadData <T >(byte [] bytes, ref int indexwhere T : BaseData, new () { T value = new T(); index += value .Reading(bytes,index); return value ; } } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 using System.Text;namespace NetLearn.Data { public class TestInfo : BaseData { public short lev; public PlayerInfo p; public int hp; public string name; public bool sex; public override int GetBytesNum () { return 2 + p.GetBytesNum() + 4 + 4 + Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name).Length + 1 ; } public override byte [] Writing () { int index = 0 ; byte [] bytes = new byte [GetBytesNum()]; WriteShort(bytes,lev,ref index); WriteData(bytes,p,ref index); WriteInt(bytes,hp,ref index); WriteString(bytes,name,ref index); WriteBool(bytes,sex,ref index); return bytes; } public override int Reading (byte [] bytes, int beginIndex = 0 { int index = beginIndex; lev = ReadShort(bytes, ref index); p = ReadData<PlayerInfo>(bytes, ref index); hp = ReadInt(bytes, ref index); name = ReadString(bytes, ref index); sex = ReadBool(bytes, ref index); return index - beginIndex; } } public class PlayerInfo : BaseData { public int atk; public override int GetBytesNum () { return 4 ; } public override byte [] Writing () { int index = 0 ; byte [] bytes = new byte [GetBytesNum()]; WriteInt(bytes, atk, ref index); return bytes; } public override int Reading (byte [] bytes, int beginIndex = 0 { int index = beginIndex; atk = ReadInt(bytes, ref index); return index -= beginIndex; } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 TestInfo info = new TestInfo(); info.lev = 87 ; info.p = new Data.PlayerInfo(); info.p.atk = 11 ; info.hp = 111 ; info.name = "hello" ; info.sex = false ; byte [] infoByte = info.Writing();TestInfo info2 = new (); info2.Reading(infoByte); print(info2.lev); print(info2.p.atk); print(info2.name);
Socket的重要API Socket的作用 Socket是C#提供的用于网络通讯的类,其他语言也有对应的概念
是支持TCP/IP网络通信的基本操作单位
可以被视为一个通道,连接于客户端与服务端,数据的发送和接受均通过这个通道
类型 流套接字 用于实现TCP通信
数据报套接字 用于实现UDP通信
原始套接字 我们使用Socket的构造函数声明不同的套接字
1 2 Socket socketTcp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Stream,ProtocolType.Tcp); Socket socketUdp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Dgram,ProtocolType.Udp);
常用属性 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 PFCLog.Info(socketTcp.Connected); PFCLog.Info(socketTcp.SocketType); PFCLog.Info(socketTcp.ProtocolType); PFCLog.Info(socketTcp.AddressFamily); PFCLog.Info(socketTcp.Available);
常用方法 常用于服务端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1" ), 8080 ); socketTcp.Bind(ipPoint); socketTcp.Listen(10 ); socketTcp.Accept();
常用语客户端 1 socketTcp.Connect(ipPoint);
常用于服务端和客户端 1 2 3 socketTcp.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); socketTcp.Close();
Socket套接字TCP通信概述 服务端和客户端需要做什么 服务端
创建Socket
用Bind方法将套接字与本地地址绑定
用Listen监听
用Accept方法等待客服端连接
建立连接,Accept返回新套接字
用Send和Receive相关方法发送数据
用shutdown释放连接
关闭套接字
客户端
创建Socket
用Connect方法与服务端连接
用Send和Receive相关方法发送数据
用shutdown释放连接
关闭套接字
服务端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 using System;using System.Net;using System.Net.Sockets;using System.Text;namespace ServerLearn { public class Server { static void Main (string [] args { Socket socketTcp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); try { IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1" ), 8080 ); socketTcp.Bind(ipPoint); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); return ; } socketTcp.Listen(1024 ); Console.WriteLine("服务端绑定监听结束,等待客户端" ); Socket socketClinet = socketTcp.Accept(); socketClinet.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("欢迎连入服务端" )); byte [] result = new byte [1024 ]; int receiveNum = socketClinet.Receive(result); Console.WriteLine($"接收到了{socketClinet.RemoteEndPoint.ToString} 发来的消息:{Encoding.UTF8.GetString(result, 0 , receiveNum)} " ); socketClinet.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); socketClinet.Close(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
客户端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 using System.Net;using System.Net.Sockets;using System.Text;using PurpleFlowerCore;using UnityEngine;namespace NetLearn { public class Lesson6 : MonoBehaviour { private void Start () { Socket socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1" ),8080 ); try { socket.Connect(ipPoint); } catch (SocketException e) { if (e.ErrorCode is 10061 ) PFCLog.Info("服务器拒绝连接" ); else PFCLog.Info("连接失败:" +e.ErrorCode); throw ; } byte [] receiveBytes = new byte [1024 ]; int receiveNum = socket.Receive(receiveBytes); PFCLog.Info("收到服务端发来的消息" +Encoding.UTF8.GetString(receiveBytes,0 ,receiveNum)); socket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("你好,我是一个客户端" )); socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); socket.Close(); } } }
服务端综合练习 我们需要实现服务端与多个客户端连接
Accept方法是可以多次调用的,且为阻塞方法,所以我们可以专门开一个线程负责客户端的连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private static void AcceptClientConnect (){ while (true ) { Socket clientSocket = _socket.Accept(); _clientSockets.Add(clientSocket); clientSocket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("欢迎连入服务端" )); } }
同理,我们还需要一个线程管理接收消息,如果服务端接收了一个客户端的消息,又需要一个线程来处理消息,此时我们可以使用线程池
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private static void ReceiveMsg (){ Socket clientSocket; int receiveNum; byte [] result = new byte [1024 *1024 ]; int i; while (true ) { for (i = 0 ; i < _clientSockets.Count; i++) { clientSocket = _clientSockets[i]; if (clientSocket.Available>0 ) { receiveNum = clientSocket.Receive(result); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(HandleMsg, (clientSocket, Encoding.UTF8.GetString(result, 0 , receiveNum))); } } } } private static void HandleMsg (object obj{ (Socket s,string str) info = ((Socket s,string str))obj; Console.WriteLine($"收到客户端{info.s.RemoteEndPoint} 发来的消息:{info.str} " ); }
用这个思路,服务端如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 using System;using System.Net;using System.Net.Sockets;using System.Text;namespace ServerLearn { public class Server { private static Socket _socketTcp; private static List<Socket> _clientSockets = new (); private static bool isClose = false ; static void Main (string [] args { _socketTcp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); try { IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1" ), 8080 ); _socketTcp.Bind(ipPoint); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); return ; } _socketTcp.Listen(1024 ); Console.WriteLine("服务端绑定监听结束,等待客户端" ); Thread acceptThread = new Thread(AcceptClientConnect); acceptThread.Start(); Thread receiveThread = new Thread(ReceiveMsg); receiveThread.Start(); while (true ) { string input = Console.ReadLine(); if (input is "Quit" ) { isClose = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < _clientSockets.Count; i++) { _clientSockets[i].Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _clientSockets[i].Close(); } _clientSockets.Clear(); break ; }else if (input.Substring(0 ,2 ) is "B:" ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < _clientSockets.Count; i++) { _clientSockets[i].Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(input.Substring(2 ))); } } } } private static void AcceptClientConnect () { while (!isClose) { Socket clientSocket = _socketTcp.Accept(); _clientSockets.Add(clientSocket); clientSocket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("欢迎连入服务端" )); } } private static void ReceiveMsg () { Socket clientSocket; int receiveNum; byte [] result = new byte [1024 *1024 ]; int i; while (!isClose) { for (i = 0 ; i < _clientSockets.Count; i++) { clientSocket = _clientSockets[i]; if (clientSocket.Available>0 ) { receiveNum = clientSocket.Receive(result); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(HandleMsg, (clientSocket, Encoding.UTF8.GetString(result, 0 , receiveNum))); } } } } private static void HandleMsg (object obj { (Socket s,string str) info = ((Socket s,string str))obj; Console.WriteLine($"收到客户端{info.s.RemoteEndPoint} 发来的消息:{info.str} " ); } } }
现在,我们用面向对象思想对服务端进行封装
ServerSocket.cs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 using System.Net.Sockets;using System.Net;namespace ServerLearn { public class ServerSocket { private Socket _socket; private Dictionary<int , ClientSocket> _clinets = new (); private bool _isClose; public void Start (string ip,int port,int num { _isClose = false ; _socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); IPEndPoint ipPoint = new (IPAddress.Parse(ip), port); _socket.Bind(ipPoint); _socket.Listen(num); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(Accept); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(Receive); } private void Accept (object obj { while (!_isClose) { try { Socket clientSocket = _socket.Accept(); ClientSocket client = new (clientSocket); _clinets.Add(client.ID, client); client.Sent("欢迎连入服务器" ); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); throw ; } } } private void Receive (object obj { while (!_isClose) { if (_clinets.Count>0 ) { try { foreach (ClientSocket client in _clinets.Values) { client.Received(); } }catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); } } } } public void Close () { _isClose=true ; foreach (ClientSocket client in _clinets.Values) { client.Close(); } _clinets.Clear(); _socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _socket.Close(); _socket = null ; } public void BroadCast (string info { foreach (ClientSocket client in _clinets.Values) { client.Sent(info); } } } }
我发现当多个客户端连入,52行会报错,原因是保存客户端的字典被更改了,唐老师似乎没有发现这个问题
所以我加了一个try-catch以防止程序崩溃
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 using System.Text;using System.Net.Sockets;namespace ServerLearn { public class ClientSocket { private static int CLIENT_COUNT = 0 ; private Socket _socket; private int _clientID; public int ID => _clientID; public ClientSocket (Socket socket ) { CLIENT_COUNT++; this ._socket = socket; _clientID = CLIENT_COUNT; } public void Close () { if (_socket is not null ) { _socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _socket.Close(); _socket = null ; } } public void Sent (string info { if (_socket is not null ) { try { _socket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(info)); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Close(); throw ; } } } public void Received () { if (_socket is null ) return ; try { if (_socket.Available>0 ) { byte [] result = new byte [1024 * 5 ]; int receiveNum = _socket.Receive(result); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MsgHandle, Encoding.UTF8.GetString(result, 0 , receiveNum)); } } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Close(); throw ; } } private void MsgHandle (object obj { string str = obj as string ; Console.WriteLine($"收到客户端{_socket.RemoteEndPoint} 发来的消息:{str} " ); } } }
客户端综合练习 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Net;using System.Net.Sockets;using System.Text;using System.Threading;using PurpleFlowerCore;namespace NetLearn { public class NetManager : Singleton <NetManager > { private Socket _socket; private Queue<string > _sendMessages = new (); private Queue<string > _receiveMessages = new (); private Thread _sendThread; private Thread _receiveThread; private byte [] _receiveBytes = new byte [1024 * 1024 ]; private int _receiveNum; private bool _isConnected; public void Connect (string ip, int port { if (_isConnected) return ; _isConnected = true ; _socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip),port); try { _socket.Connect(ipPoint); _sendThread = new (SendMessage); _receiveThread = new (ReceiveMessage); _sendThread.Start(); _receiveThread.Start(); } catch (SocketException e) { if (e.ErrorCode == 10061 ) { PFCLog.Info("服务器拒绝连接" ); throw ; } Console.WriteLine(e); throw ; } } public void Send (string info { _sendMessages.Enqueue(info); } public void Receive () { if (_receiveMessages.Count > 0 ) { PFCLog.Info(_receiveMessages.Dequeue()); } } private void SendMessage () { while (_isConnected) { if (_sendMessages.Count > 0 ) { _socket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(_sendMessages.Dequeue())); } } } private void ReceiveMessage () { while (_isConnected) { if (_socket.Available <= 0 ) continue ; _receiveNum = _socket.Receive(_receiveBytes); _receiveMessages.Enqueue(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(_receiveBytes,0 ,_receiveNum)); } } public void Close () { _isConnected = false ; if (_socket is not null ) { _socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _socket.Close(); } } ~NetManager() { Close(); } } }
区分消息类型 我们之前发送的消息都是string,这显然不够。现在,我们要区分消息的类型。
比如,我们要发送类对象数据,就可以使用上文 所写的数据类,问题在于,另一端如何知道我们发送的具体是什么类型的对象
如何区分消息 我们可以给消息添加一个标识,比如在所有消息的头部添加一个消息id,然后消息的接收方先检查消息的id,根据id区分消息
现在我们修改此前写的客户端的NetManager和服务端的ClientSocket
NetManager 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Net;using System.Net.Sockets;using System.Threading;using NetLearn.Data;using PurpleFlowerCore;namespace NetLearn { public class NetManager : Singleton <NetManager > { private Socket _socket; private Queue<BaseMsg> _sendMessages = new (); private Queue<BaseMsg> _receiveMessages = new (); private Thread _sendThread; private Thread _receiveThread; private byte [] _receiveBytes = new byte [1024 * 1024 ]; private int _receiveNum; private bool _isConnected; public void Connect (string ip, int port { if (_isConnected) return ; _isConnected = true ; _socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip),port); try { _socket.Connect(ipPoint); _sendThread = new (SendMessage); _receiveThread = new (ReceiveMessage); _sendThread.Start(); _receiveThread.Start(); } catch (SocketException e) { if (e.ErrorCode == 10061 ) { PFCLog.Warning("服务器拒绝连接" ); throw ; } Console.WriteLine(e); throw ; } } public void Send (BaseMsg info ) { _sendMessages.Enqueue(info); } public void Receive () { if (_receiveMessages.Count > 0 ) { BaseMsg msg = _receiveMessages.Dequeue(); if (msg is TestMsg1) { TestMsg1 testMsg1 = msg as TestMsg1; PFCLog.Info("收到消息:" +testMsg1.info.atk); } } } private void SendMessage () { while (_isConnected) { if (_sendMessages.Count > 0 ) { _socket.Send(_sendMessages.Dequeue().Writing()); } } } private void ReceiveMessage () { while (_isConnected) { if (_socket.Available <= 0 ) continue ; _receiveNum = _socket.Receive(_receiveBytes); int msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(_receiveBytes, 0 ); BaseMsg msg = null ; switch (msgID) { case 1001 : msg = new TestMsg1(); msg.Reading(_receiveBytes, 4 ); break ; } if (msg is null ) { PFCLog.Warning("未知消息:" +msgID); continue ; } _receiveMessages.Enqueue(msg); } } public void Close () { _isConnected = false ; if (_socket is not null ) { _socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _socket.Close(); } } ~NetManager() { Close(); } } }
ClientSocket 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 using System.Text;using System.Net.Sockets;using NetLearn.Data;namespace ServerLearn { public class ClientSocket { private static int CLIENT_COUNT = 0 ; private Socket _socket; private int _clientID; public int ID => _clientID; public ClientSocket (Socket socket ) { CLIENT_COUNT++; this ._socket = socket; _clientID = CLIENT_COUNT; } public void Close () { if (_socket is not null ) { _socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _socket.Close(); _socket = null ; } } public void Sent (BaseMsg info ) { if (_socket is not null ) { try { _socket.Send(info.Writing()); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Close(); throw ; } } } public void Received () { if (_socket is null ) return ; try { if (_socket.Available>0 ) { byte [] result = new byte [1024 * 5 ]; int receiveNum = _socket.Receive(result); int msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(result, 0 ); BaseMsg msg = null ; switch (msgID) { case 1001 : msg = new TestMsg1(); msg.Reading(result, 4 ); break ; } if (msg is null ) { Console.WriteLine("未知消息:" +msgID); return ; } ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MsgHandle, msg); } } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Close(); throw ; } } private void MsgHandle (object obj { BaseMsg msg = obj as BaseMsg; if (msg is TestMsg1) { Console.WriteLine($"收到客户端{_socket.RemoteEndPoint} 发来的消息:{(msg as TestMsg1).info.atk} " ); } } } }
分包、粘包 什么是分包和粘包 分包、粘包指网络通信中由于各种因素(网络环境、API规则)造成的消息与消息之间出现的两种状态
分包:一个消息分成了多个消息进行发送
粘包:一个消息和另一个消息黏在了一起
如何解决分包和粘包 现在,我们没有考虑分包粘包的情况,反序列化有可能出问题
为了解决分包粘包,首先,我们需要判断是否发生了分包粘包,也就是判断消息的长度
为消息添加头部,头部记录消息的长度
当我们接受到消息的时候,通过长度来判断是否分包和粘包
对消息进行拆分合并处理,然后处理完成的消息
我在想,如果分包或粘包的地方是消息的头部,我们现在的头部有8个字节,我们还要处理头部的分包粘包,才能处理消息的分包粘包. 那么,字节可以分包粘包吗,我的意思比如说是一次传输了4个比特,下一次传输了12个比特,这样要处理的情况就更复杂了
首先,我们更改此前写的TestMsg1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 ... public override byte [] Writing () { int index = 0 ; byte [] bytes = new byte [GetBytesNum()]; WriteInt(bytes,GetID(),ref index); WriteInt(bytes,GetBytesNum()-8 ,ref index); WriteInt(bytes, num, ref index); WriteData(bytes,info,ref index); return bytes; } public override int GetBytesNum () { return 4 + 4 + 4 + info.GetBytesNum(); } ...
和NetManager
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 ``` private void ReceiveMessage () { while (_isConnected) { if (_socket.Available <= 0 ) continue ; byte [] receiveBytes = new byte [1024 * 1024 ]; int receiveNum = _socket.Receive(receiveBytes); HandleReceiveMsg(receiveBytes,receiveNum); } } private void HandleReceiveMsg (byte [] receiveBytes,int receiveNum { int msgID = 0 ; int msgLength; int nowIndex = 0 ; receiveBytes.CopyTo(_cacheBytes,_cacheNum); _cacheNum += receiveNum; while (true ) { msgLength = -1 ; if (_cacheNum -nowIndex >= 8 ) { msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(_cacheBytes, nowIndex); nowIndex += 4 ; msgLength = BitConverter.ToInt32(_cacheBytes, nowIndex); nowIndex += 4 ; } if (_cacheNum - nowIndex >= msgLength&& msgLength!=-1 ) { BaseMsg msg = null ; switch (msgID) { case 1001 : msg = new TestMsg1(); msg.Reading(_cacheBytes, nowIndex); break ; } if (msg is not null ) _receiveMessages.Enqueue(msg); nowIndex += msgLength; if (nowIndex == _cacheNum) { _cacheNum = 0 ; break ; } } else { if (msgLength != -1 ) { nowIndex -= 8 ; Array.Copy(_cacheBytes,nowIndex,_cacheBytes,0 ,_cacheNum-nowIndex); _cacheNum -= nowIndex; } break ; } } } ```
客户端主动断开连接 目前在客户端主动退出时,我们会调用socket的shutdown和close方法,但这样做服务端无法得知客户端断开连接
于是我们需要解决目前断开不及时的问题
首先,我们定义一种消息类型专门用来表示客户端断开连接,客户端发送该消息,服务端接收到该消息后,就在ServerSocket中把该客户端从字典中移除
注意线程安全问题
实现心跳消息 什么是心跳消息 心跳消息指的是长连接中,客户端和服务端之间定期发送的一种特殊的数据包,用于通知对方自己还在线,以确保长连接的有效性
为什么需要心跳消息
实现心跳消息